Turntables
In this experiment you will explore the penetrating power of different types of radiation. A Geiger counter is used to measure the radiation coming from four different radioactive sources, which can be selected by rotating a turntable. A second turntable can be used to place four different types of absorbers between the radioactive source and the detector.
| Take me to the Turntables |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Inverse Square Law
The further you are away from a radioactive source, the better! This experiment will demonstrate how the amount of radiation decreases with increasing distance from the source. A Geiger counter is used to measure the radiation coming from a real radiation source at a distance selected by you.
| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Decay
Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atom emits energy in the form of radiation. This experiment will explore the statistical (random) nature of radioactive decay.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Photoelectric Effect
In this activity you will re-create the famous Photoelectric Effect, the process in which metals can eject electrons when light is shined upon them. Explore how light of different wavelengths and intensities can be used create electricity, and decide for yourself if light behaves like a wave or a particle.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
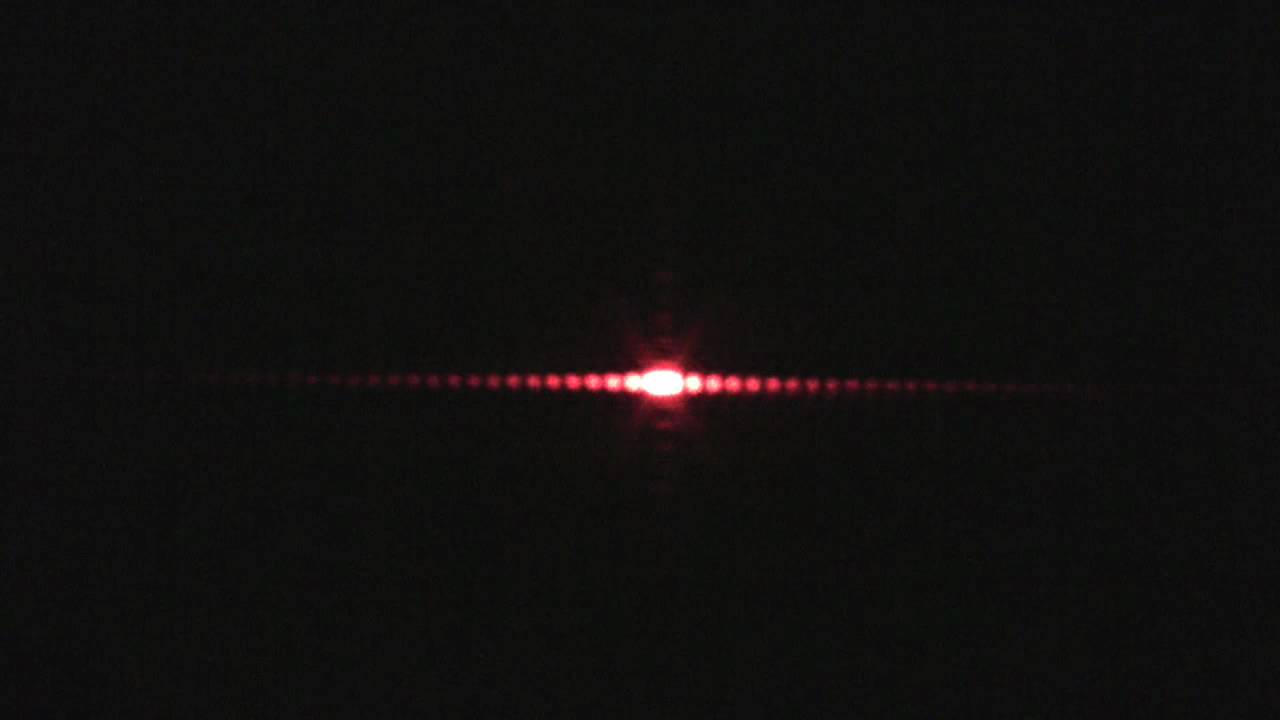
Diffraction
In this activity you will shine a laser of known wavelength onto a copper wire and record a light intensity profile, with peaks and troughs being present you can determine the thickness of a wire. Explore how light is capable of diffraction and bending around thin objects in order to determine the width of objects far beyond the capabilities of the human eye and other current technology.
| Take me to the Turntables |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Thin Lens
Lens are useful optical devices for exploring the ray behaviour of light, such as refraction and reflection. In this experiment students will determine the focal point of converging and diverging lens' and describe the formed images as real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished.
| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
3D Imaging
In this experiment you will learn about x-ray imaging and how it is used in the research and medical industries. The main focus of this activity is introducing the concept of 3D imaging and how you can build a 3D image of an object by taking a set of regular 2D images and rotating the object between exposures. In the medical industry, a 3D image is commonly referred to as a CT scan (Computed Tomography Scan) or CAT Scan (Computer Axial Tomography Scan). You will learn how the number of 2D projections affects the quality of the 3D image, and the balance that doctors must strike between taking a good quality 3D image (lots of 2D images) while limiting the patient’s exposure to x-rays.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Make a Telescope
Lens are useful optical devices for exploring the ray behaviour of light, such as refraction and reflection. In this experiment students will determine the focal point of converging and diverging lens' and describe the formed images as real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
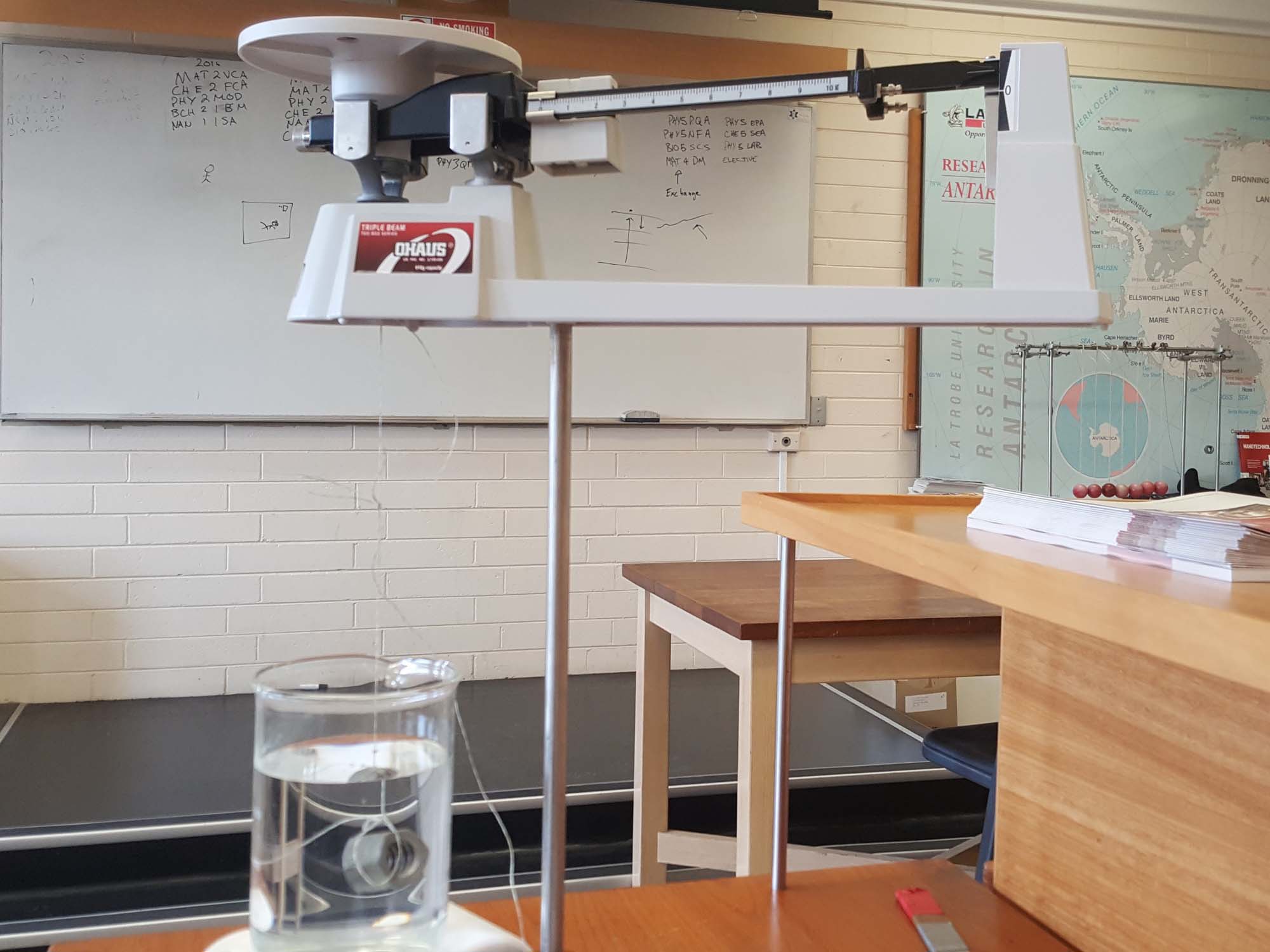
Archimedes Principle
Students will use Archimedes' Principle to investigate bouyancy an an upward force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
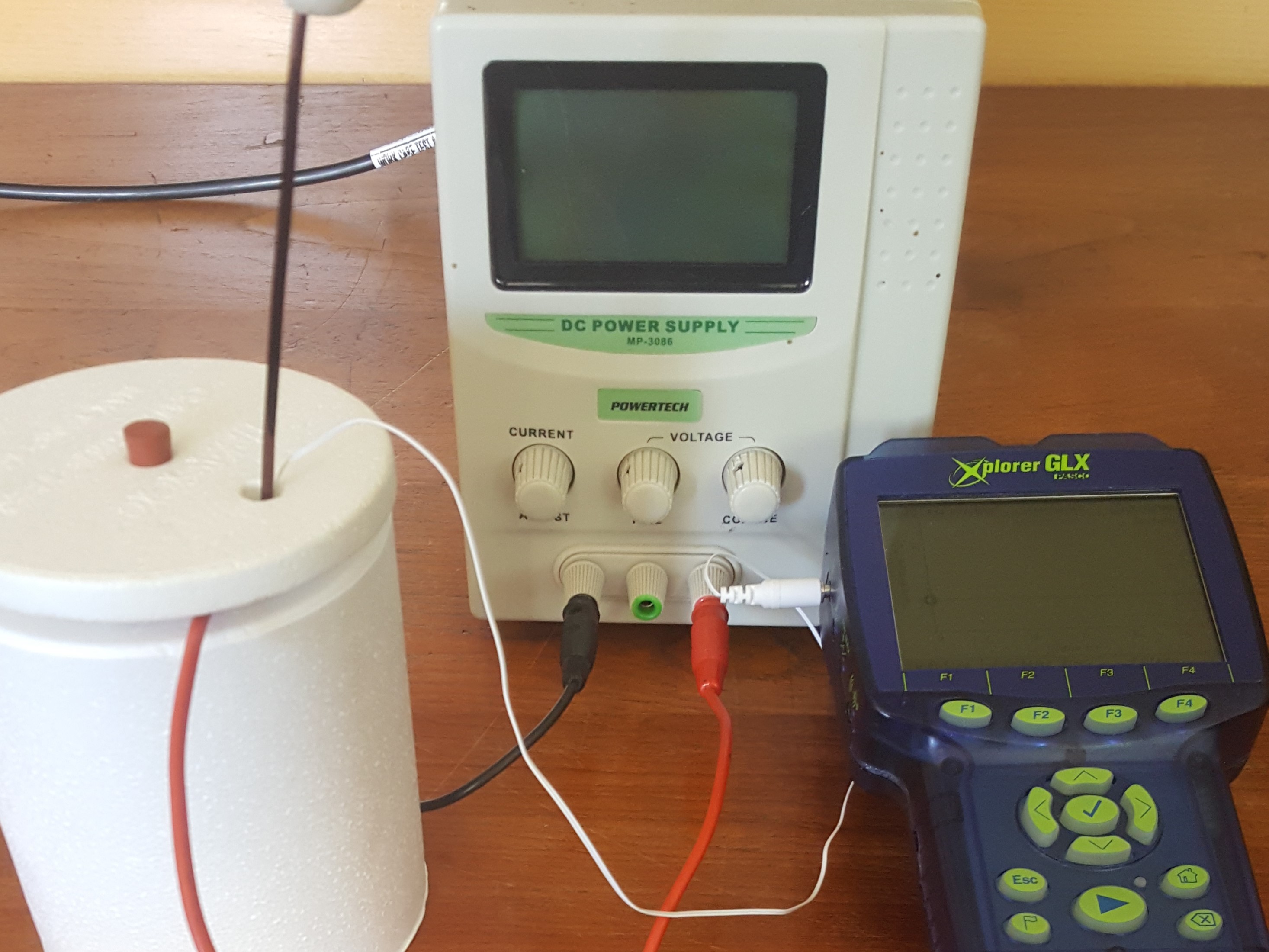
Calorimetry
Students investigate the thermodynamic process of heat transfer when a substance undergoes a phase change.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Simple Pendulum
A simple pendulum consists of a mass suspended by a (massless un-stretchable) string. When the mass or bob is pulled to one side and then released it oscillates about the equilibrium position. In this experiment students investigate the effects of mass and length of the pendulum lever on the period and speed of oscillation.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Spring Constant
This experiment investigates the compression and expansion of an ideal spring using Hookes Law.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
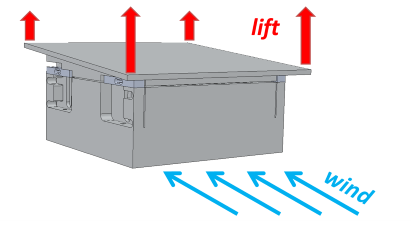
Wind Tunnel
Explore aerodynamic lift and drag by controlling an aerofoil in a real wind tunnel!


| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |
Magnetic Induction
In this experiment students will observe the relationship between the magnitude of the induced EMF and the applied magnetic field by varying a magnetic field over time by passing current through coils of wire.

| Take me to the Experiment |
| Explore the Simulated Experiment |
| Further Information, and Quiz |