Virtual Lab - Spring Constant
An ideal spring obeys Hooke’s Law. Hooke’s Law states that the force from a spring is proportional to, and in the
opposing direction to, the displacement of the free end. This can be written as
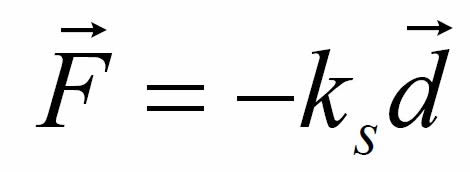
d is the displacement of the free end of the spring,
ks is known as the spring constant and,
the minus sign indicates that the Force imposed by the spring is in the opposite direction to the displacement.
To conduct this virtual experiment;
Click the buttons on the right to add the corresponding weight to the spring shown in the experimental image.
Examine the extension of the spring, and tabulate your results in the table below, then click plot to plot your data.

| Weight | Weight Force (Newton) | Displacement (Millimetres) | |
| No Weight | |||
| Weight 1 - 50 Grams | |||
| Weight 2 - 100 Grams | |||
| Weight 3 - 150 Grams | |||
| Weight 4 - 200 Grams | |||
| Weight 5 - 250 Grams | |||
| Weight 6 - 300 Grams | |||
| Weight 7 - 350 Grams | |||
| Weight 8 - 400 Grams |




